Our office is equipped with the latest diagnostic equipment and tests to determine if there is a retinal problem we need to address. Once testing is complete, your doctor will discuss your results and possible treatment options with you. Our exceptional care includes offering the following advanced tests.
Fluorescein Angiography
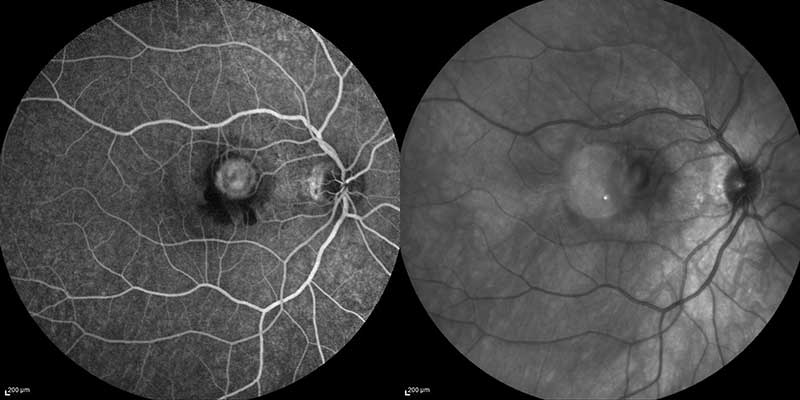
fluorescein angiogram and infrared fundus photo of choroidal neovascular membrane
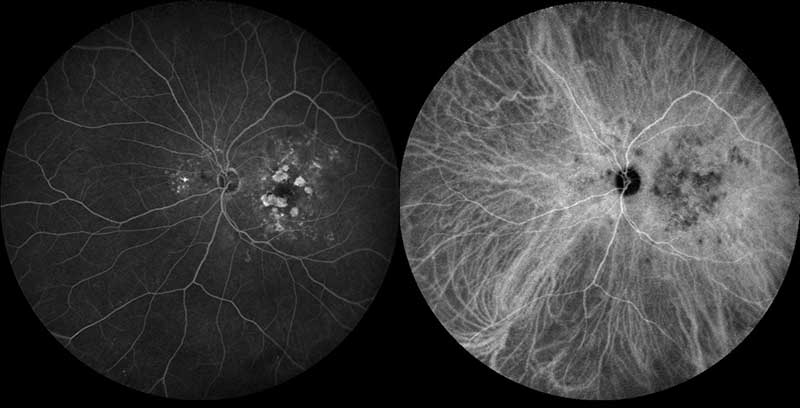
normal fluorescein angiogram photo with infrared fundus photo
Fluorescein Angiography (FA) is a diagnostic test that utilizes a specialized camera and a fluorescein dye to analyze the blood supply to the retina. During the test, the fluorescein dye is injected into a peripheral vein, usually in the hand or arm; the dye then passes through the blood vessels in the retina. An ophthalmic technician will take a series of time-dependent photographs as the dye travels through the blood vessels in the retina. The images captured will be in black and white, with the dye showing up as light grey or white areas of brightness. In a healthy eye, the retinal blood vessels and pigment layer of the retina (retinal pigment epithelium) serve as a protective barrier, inhibiting the leakage of the fluorescein dye into the retina. Interpretation of these photos can reveal abnormal blood vessels or damage to the retinal pigment epithelium. This procedure is commonly used to diagnose and monitor the progression of many different disorders affecting the retina, including diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration and cystoid macular edema. In general, this test is very safe, but in rare cases the dye can cause allergic reactions; therefore, patients will be monitored closely during the procedure. Likewise, patients may notice yellow or green urine on the day of the procedure; this is normal and will stop within one or two days.
Indocyanine Green Angiography
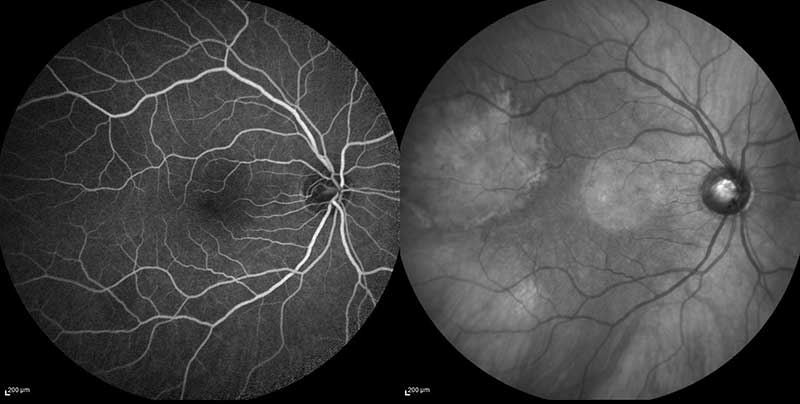
fluorescein and indocyanine green angiogram of dry macular degeneration
Indocyanine green (ICG) angiography is very similar to FA, with the main difference being that a different dye is injected into a peripheral vein. This time-dependent imaging test is used to photograph blood vessels below the retina. ICG angiography allows the retina specialist to study parts of the eye that are often difficult to visualize with FA. ICG angiography is commonly used in diagnosing and monitoring diseases such as central serous chorioretinopathy, certain forms of macular degeneration, and various inflammatory disorders. In general, ICG is very safe, but it can cause allergic reactions in patients who are allergic to iodine.
Fundus Autofluorescence
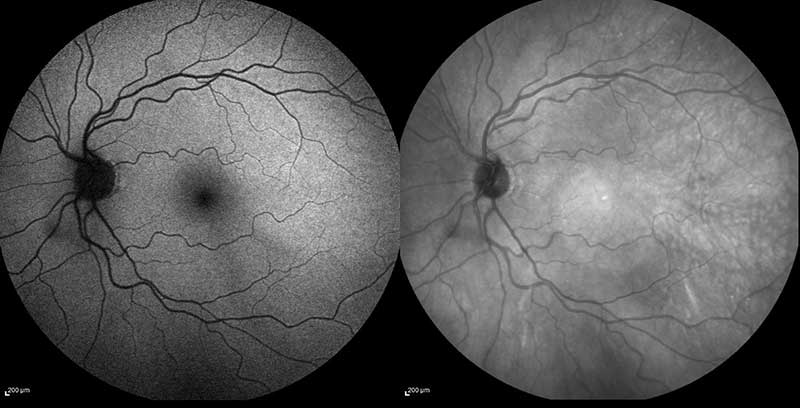
Normal autofluorescence fundus photo with infrared fundus photo
Fundus Autofluorescence (FAF) is a diagnostic imaging tool that utilizes a blue-green wavelength light to visualize conditions that affect the pigment layer of the retina (retinal pigment epithelium). FAF imaging documents deposits of fluorophores from the naturally or pathologically occurring fluorescent pigment, lipofuscin, within the retinal pigment epithelium. Lipofuscin accumulation normally increases with age, but it is also thought to increase as a result of various retinal conditions. This test is non-invasive, quick and has no known adverse effects.
Optical Coherence Tomography Imaging (OCT)
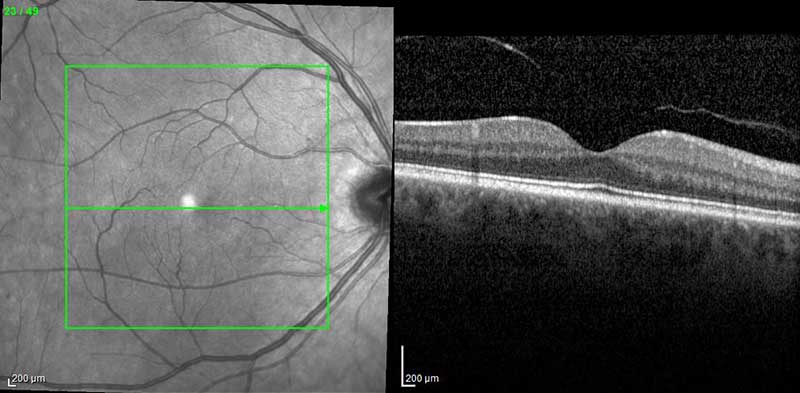
Normal infrared fundus photo with OCT of the macula
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive, diagnostic imaging technique that provides detailed and magnified cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT uses light rays to map and measure the thickness of the retina, while creating a multi-dimensional reconstruction of the retina. This test can often reveal tiny abnormal areas of the retina, macula and optic nerve. OCT is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as glaucoma, macular hole, macular edema, and diabetic retinopathy. During this test, the patient will sit in front of the OCT machine, rest his or her chin on the supportive chinrest, hold very still, and look straight ahead with eyes open at the blue light. This test has no known side effects.
High Resolution Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography
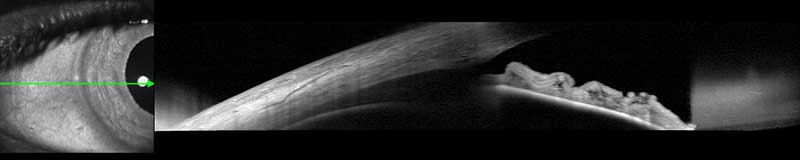
anterior segment OCT
High resolution anterior segment optical coherence tomography is a specialized form of OCT imaging that can be used to evaluate anterior structures, or those located in the front of the eye; including the cornea, iris, ciliary body and lens.
Spectralis Multi-Color Imaging
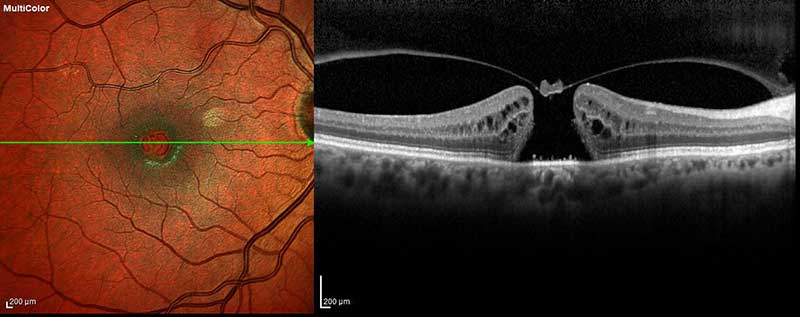
multicolor fundus photo with OCT
MultiColor imaging utilizes multiple laser colors simultaneously to capture images of different depths within the retina. This non-invasive imaging technique creates a sharper and clearer image by combining information from each continuously scanning laser. This technology also provides active, live eye-tracking and noise-reduction technology which helps to create quality photographs in difficult to image patients, such as those with cataracts or eye movement disorders. Additionally, MultiColor imaging is useful in highlighting diseases that are more difficult to identify in traditional fundus photographs.
Ultra-Widefield Photography, FA and ICG
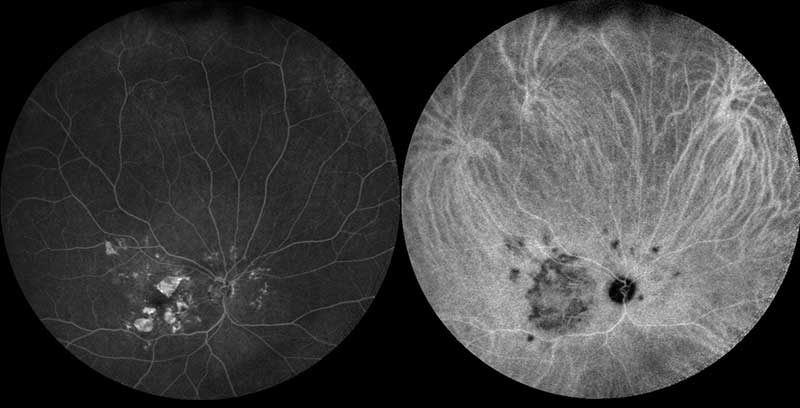
ultra-wide field fluorescein and indocyanine green angiogram of dry macular degeneration
Ultra-widefield photography allows for imaging of a much larger portion of the retina in comparison to classic retinal photography. Classic imaging methods covers only about 45 degrees, while ultra-widefield imaging allows for the viewing of almost 200 degrees, or 80% of the retina. This technique is useful in the diagnosis of abnormalities in the peripheral retina that are unable to be viewed with classic imaging techniques.
Ocular Ultrasonography
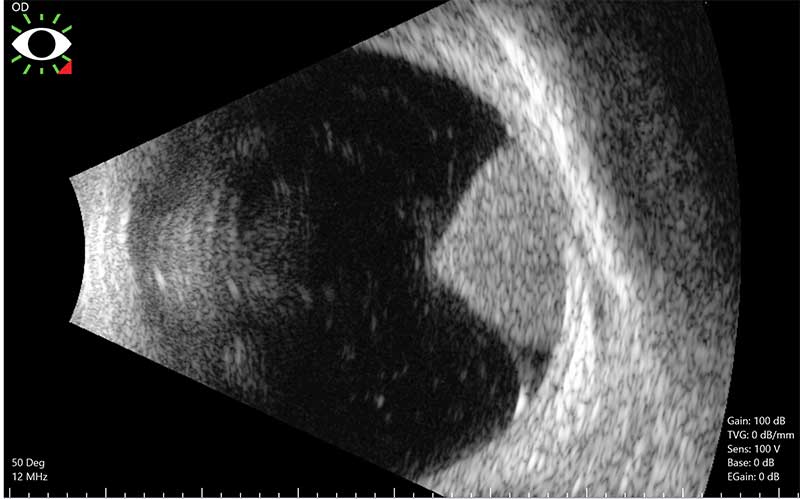
ultrasound of a choroidal melanoma
Ocular ultrasonography is a non-invasive, imaging technique that uses sound waves to improve visualization of the retina. This procedure produces a two-dimensional cross-sectional view of the eye by placing the ultrasound probe over the eye. Ultrasound is an important tool to evaluate the eye in circumstances where there is poor visibility, such as when there is eyelid swelling, poor pupil dilation, corneal scarring, an advanced cataract, or a hemorrhage in the eye. Ultrasound can also be useful to evaluate a foreign body after a traumatic injury, retinal detachment, some optic nerve findings, and even tumors of the retina and choroid (such as a choroidal melanoma). Additionally, an ocular ultrasound can also be used to visualize other structures in the eye such as the lens, choroid, sclera, and vitreous. An ocular ultrasound is helpful for both diagnosis and treatment planning, and there are no known side effects.
Digital Fundus (Retinal) Photography
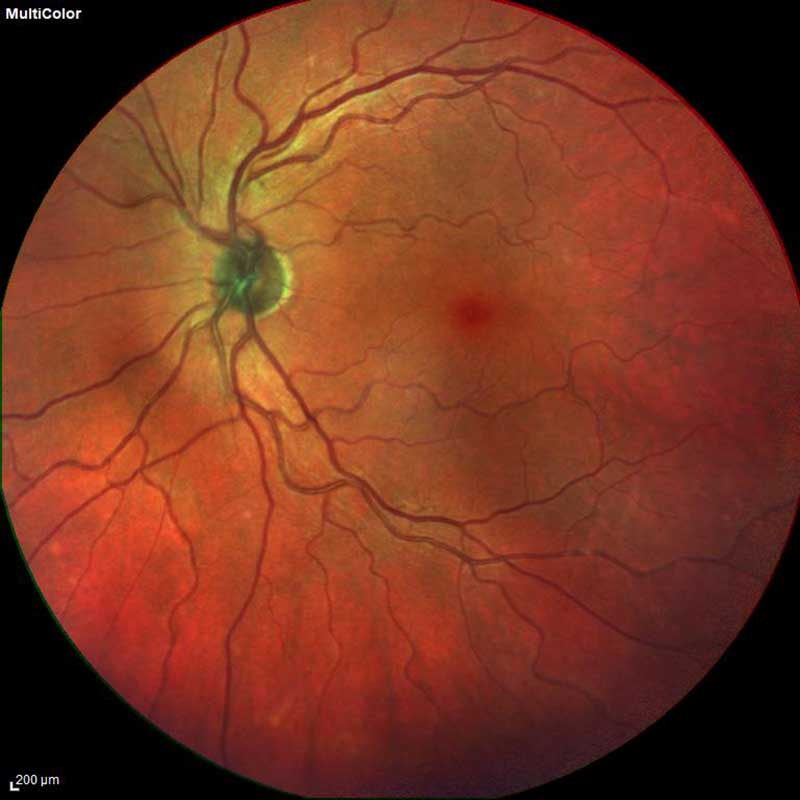
normal fundus photo
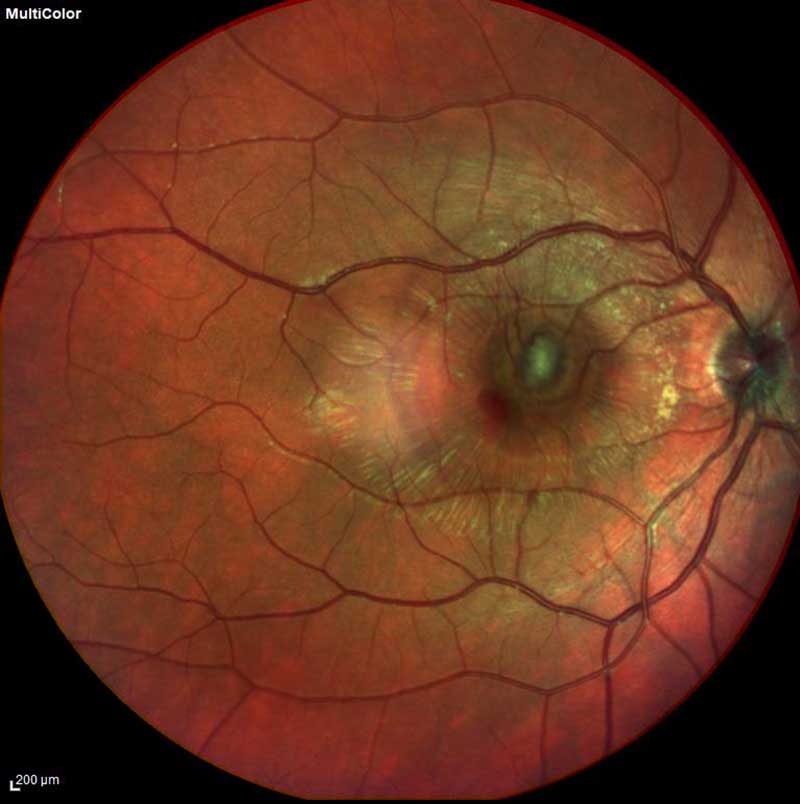
fundus photo with choroidal neovascular membrane
Digital fundus photography is a form of advanced retinal photography. This diagnostic procedure creates a clear image of the optic nerve, blood vessels, macula and fovea. Fundus photos are often used as a baseline measurement for future comparison. Digital fundus photos are commonly used in the early detection and diagnosis of diseases such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and retinal detachments.